
Experts in Spray Drying Creating custom equipment for all your spray drying needs
 Spray drying is an advanced technology that converts a solution or liquid into a solid powder in just one step.
This is achieved through the atomization of a liquid into a spray, or fine mist of droplets.
These droplets are then met with a stream of hot air that causes evaporation and reduces the mist to a dried powder form.
Spray drying is an advanced technology that converts a solution or liquid into a solid powder in just one step.
This is achieved through the atomization of a liquid into a spray, or fine mist of droplets.
These droplets are then met with a stream of hot air that causes evaporation and reduces the mist to a dried powder form.
By atomizing a liquid, a large surface area is created which can then be dried more rapidly and thoroughly. This method of spray drying is more consistent, more thorough, and can be performed at lower temperatures, allowing substances to better retain their natural properties (i.e. flavor in food products).
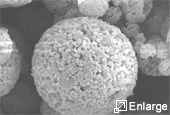
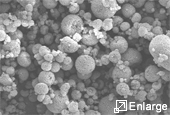
Create incredibly fine powder of only 5 to 15 microns, in small scale or bulk quantities.
High-volume, large-capacity production of incredibly fine powder with is made possible through GF Corporation’s Micro Mist Spray Dryer.
Decrease residence time inside the equipment.
Our spray dryers eliminate the need for bulky drying beds that require space and extend the length of the drying process.
Accelerate your production through the uninterrupted use of our state-of the-art non-clogging nozzle.
Smooth and continuous spray of highly viscous liquid, up to 5000cp, is made possible through external mixing.
- Reduce the scale of your equipment space requirements with our compact and efficient design.
- Increase heat efficiency by setting the exhaust temperature low.
Eliminate the need for the pulverizing and classifying processes.
- Create dried powder in fewer steps; Minimize undried/agglomerated particles;
eliminate unwanted stickiness / moisture.
- Dry materials that are difficult to dry when using other drying techniques.
- Dry by reacting two liquids through the use of GF Corporation’s Four Nozzle System.
- Dry materials at low temperatures (below boiling point) to preserve material properties
(particularly helpful for the Food Industry).
- Create uniform powder with very narrow particle size distribution.
- Control and adjust the droplet median diameter by changing gas-liquid ratio.
- Dry by combining two different liquids using the Four Fluid Nozzle System.
- Increase user convenience with the Central Control Panel and Viewing Chamber.
- Reduce cleaning time through easy disassembly and setup of removable parts
(MMSD uses external mixing which also reduces the need for extensive cleaning of multiple parts as required by other spray dryers).
| MMSD-Micro Mist Spray Dryer | Other Spray Dryers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nozzle Type | Four Fluid Nozzle | Two Fluid Nozzle | Pressure Nozzle | Rotary Atomizer |
| Droplet Particle Diameter | Fine particle | Fine particle | Coarse particle | Coarse particle |
| 5 - 15µm | 5 - 30µm | 0 - 150µm | 10 - 100µm | |
| Atomization Uniformity | Even | Uneven | Slightly Uneven | Even |
| Method of Atomization | Compressed Gas | Compressed Gas | Pressurizing Pump | Motor |
| Atomization Energy | High | High | Low | Low |
| Liquid Processing Capacity per Nozzle | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Capacity for Droplet Diameter Control | ◎ | △ | △ | ◎ |
| High (at fine particle range) | Conditions Apply | Conditions Apply | High | |
| Countermeasure against Viscosity Change | Air Pressure | Air Pressure | Fluid Pressure | Revolution |
| Ability to spray High-Viscosity Liquids | ◎ | ○ | × | ○ |
| Great | Mediocre | Incapable | Mediocre | |
| Maintainability | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | △ |
| High | High | Medium | Conditions Apply | |
| Spray Angle | 180° | Under 30° | Under 60° | 180° |
| Spray Shape | Hollow cone | Hollow cone fine | Full cone fine | Hollow cone |
GF Corporation will provide support and guidance from experimentation to the designing, manufacturing, and maintaining of your customized production machine. All Micro Mist Spray Dryers are designed to allow you to easily and cost-effectively scale up from small scale to commercial scale.
| MMSD-Micro Mist Spray Dryer | Conventional Spray Dryer | |
|---|---|---|
| Atomization Device | Four Fluid Nozzle | Two Fluid Nozzle, Rotary Atomizer |
| Nozzles required to Atomize a small amount | One Nozzle | One Nozzle |
| Nozzles required to Atomize a large amount | One Nozzle | Multiple Nozzles |
| Scale-up Potential | Designed to scale up easily Laboratory units are used to test issues and parameters for convenient scaling up |
Scaling up is more problematic because of the multiple nozzles Issues such as gas-flow turbulence and droplet collision make scaling up a more difficult process |
| Drying Efficiency | Incredible drying efficiency through the use of the 180° hollow cone which eliminates unevenness in hot air contact | Poor drying efficiency The full cone requires much more time for droplets to contact the hot air |
| System Size | Compact: Drying chamber can be smaller due to the MMSD’s superior drying efficiency compared to the conventional spray dryers | Large: Drying chamber will be larger and require more space Uneven and less thorough drying |
| Continuous Operation | Continuous uninterrupted operation without nozzle clogging achieved through the external mixing/drying | Very high likelihood of nozzle clogging |
| Compressed Air Volume | Smaller; If the liquid processing rate is the same as a conventional spray dryer, the air flow rate of the four fluid nozzle will be less | Larger |
| Ease of Operation | Convenient and simple operation using the central touch panel control system | Generally less convenient / centralized System is complicated with many nozzles and liquid pumps |
| Maintenance | Easy maintenance and upkeep with fewer nozzles and liquid transmission pumps | Inconvenient and complex to maintain with many nozzles and liquid transmission pumps |
| Initial Cost | Competitive pricing with smaller system options available | Subject to cost increases if production becomes high-capacity |
| Running Cost / Energy Consumption | Electrical energy consumption of compressor will be 20% to 50% less | Electrical energy consumption of the compressor is huge |
| MMSD-Micro Mist Spray Dryer | Other drying methods such as milling/pulverizing | |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity for Fine Powder Manufacturing | Powder can be attained directly from the liquid | Many more steps required in the drying process When converting slurry to powder, disintegrating/pulverizing the liquid after dehydrating at the filter press and shelf drying is necessary |
| System Configuration | 1 unit | Several units |
| For use in Research & Development | Great; Powder can be easily attained | Requires more time and more steps: pulverizing and classification |
| Operating System | Continuous operation for long sets of time | Requires separate batch operation |
| Operating Performance | Simple user interface Simple assembly and clean up |
Operating knowledge is necessary for each device Washing and assembling is complex and difficult |
| Maintainability | Easy maintenance with the nozzle as the only necessary spare part | Knowledge of maintenance and spare parts is necessary for each device |
| Sanitary Factor | Highly sanitary contained system | Often unsanitary and open system |
| Initial Cost | The same or cheaper than pulverizing/milling systems once all setup costs are considered; generally a more simple system | With a broad range of devices and systems there is also a broad range in prices; could require more equipment for additional steps (air classification, etc.) |
| Operating Costs | Electrical energy required can be higher, but the machine requires less manpower to run | Often requires much more in manpower depending on the material flow between devices |
| Chance of Contamination | Zero | Extremely high |
| Fluid Capabilities | Will work with slurry and solution Ideal size for slurry particles is below 1 to 2 µm |
Will work with slurry but difficult to work with solution (increasing concentration will be necessary) |
| Product Property | Spherical form; fine powder Porous, Low density |
Formation is instable High density |
| Quality Control of the Product | Uniform product with little variation; easy to control product because there are fewer variables | Quality control is necessary on each device and ; huge range of variable factors |
| Residual Moisture | Almost every powder can observe the standard for complete drying | Sometimes final drying might be necessary |
| Control of Thermal Denaturation | Instant drying at low temperature below boiling point is possible | Extended and possibly damaging exposure to heat is required for thorough drying |